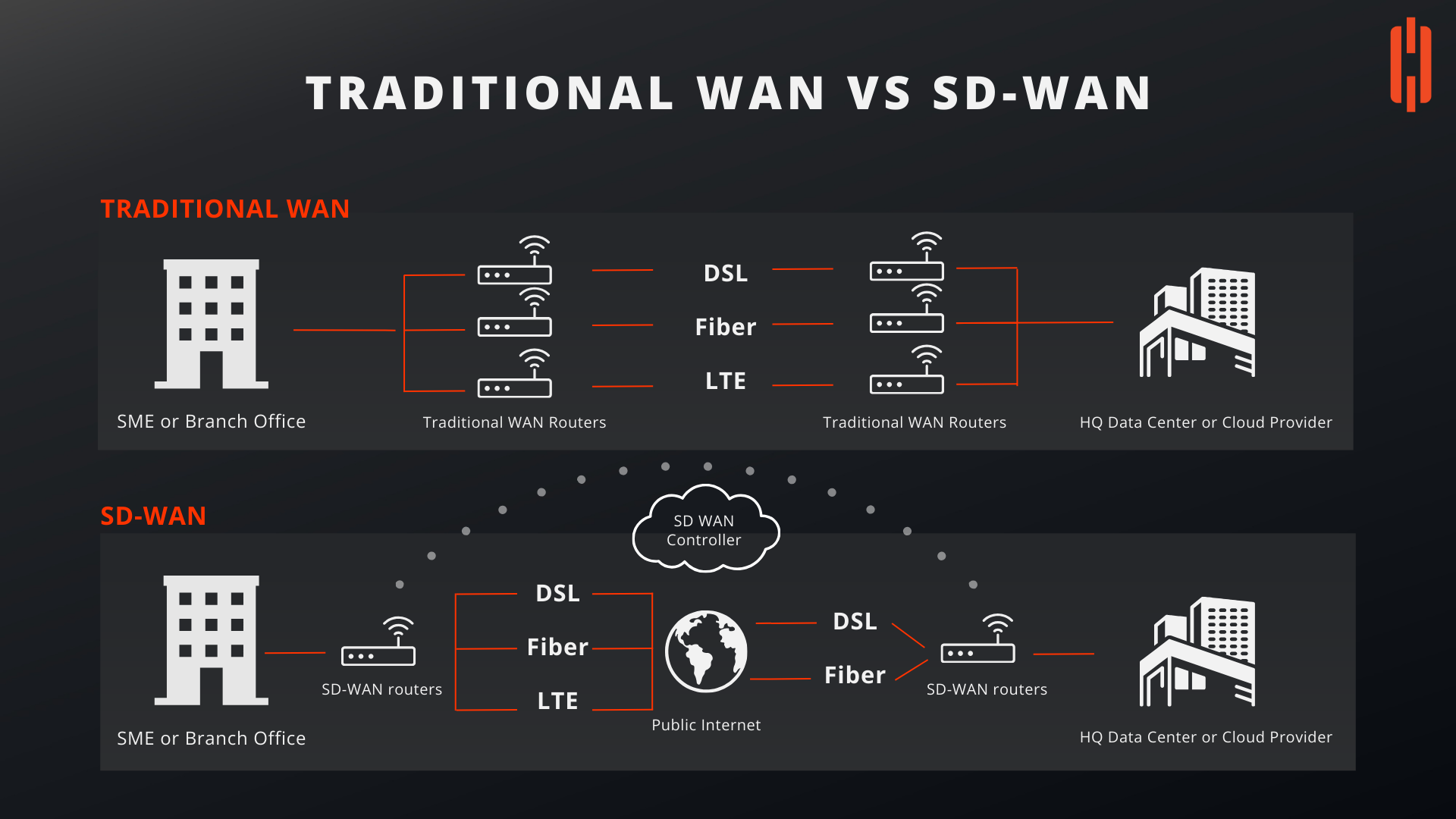
Traditional WAN vs. SD-WAN: A Comparative Overview
As organizations continue to evolve and expand their networks, the demand for more efficient, flexible, and cost-effective networking solutions has grown. This has led to the adoption of Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) as a modern alternative to traditional WAN (Wide Area Network) architectures. The image above compares these two networking approaches, highlighting key differences and advantages of SD-WAN over traditional WAN.
Traditional WAN
Traditional WAN architectures have been the standard for connecting branch offices, data centers, and headquarters for many years. However, as business needs change, the limitations of traditional WANs have become more apparent.
- Fixed Infrastructure:
- Traditional WAN relies on fixed physical connections, such as MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) circuits, to route traffic between locations. These connections are typically expensive and often require long lead times for provisioning.
- Centralized Control:
- In a traditional WAN, traffic is backhauled to a central data center or headquarters, which can create bottlenecks and increase latency, especially for cloud-based applications.
- Limited Flexibility:
- Traditional WANs are often rigid in their configuration, making it challenging to adapt to changing network demands or to prioritize different types of traffic dynamically.
- Complex Management:
- Managing a traditional WAN can be complex, requiring manual configuration of routers and other network devices at each location. This can lead to higher operational costs and increased risk of human error.
SD-WAN
SD-WAN, or Software-Defined WAN, represents a more agile and efficient approach to networking, addressing many of the challenges associated with traditional WAN.
- Software-Defined Control:
- SD-WAN decouples the network control from the physical infrastructure, allowing for centralized management through a software-defined controller. This enables dynamic routing of traffic based on current network conditions, application priorities, and business policies.
- Optimized Traffic Management:
- With SD-WAN, traffic can be routed over multiple types of connections, such as DSL, fiber, and LTE, based on real-time performance metrics. This ensures optimal application performance and can reduce latency, especially for cloud-based services.
- Cost Efficiency:
- SD-WAN leverages the public internet for connectivity, which is generally more cost-effective than traditional MPLS circuits. This allows organizations to scale their networks more affordably without sacrificing performance.
- Enhanced Security:
- SD-WAN solutions often include integrated security features, such as encryption and next-generation firewalls, providing secure connectivity across all locations without the need for additional hardware.
- Simplified Management:
- SD-WAN simplifies network management by providing a centralized platform for configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting. This reduces the operational burden on IT teams and minimizes the risk of errors.
The comparison between traditional WAN and SD-WAN highlights the significant advantages that SD-WAN offers in terms of flexibility, cost-efficiency, and performance. As organizations continue to adopt cloud services and expand their remote work capabilities, SD-WAN provides a scalable and agile solution that can adapt to evolving business needs. By shifting to SD-WAN, businesses can enhance their network performance, reduce operational complexity, and better support their digital transformation initiatives.