Platform
Platform
Everything you need to run a secure global network—in a single system.
Solutions
Solutions
Learn how our solutions were designed to help you scale your IT resources
Company
CommandLink
Let's talk about how we can help you!
Partners
What is the OSI Model and Why is it Important in Networking?
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Model is a conceptual framework used to understand and implement network protocols in seven distinct layers. It standardizes networking protocols to allow communication between different systems without requiring changes to the underlying hardware and software. Each layer of the OSI Model serves a specific function and interacts with the layers directly above and below it. The OSI Model is crucial in networking because it provides a universal set of standards for hardware and software manufacturers, ensuring interoperability and a common language for engineers and developers.
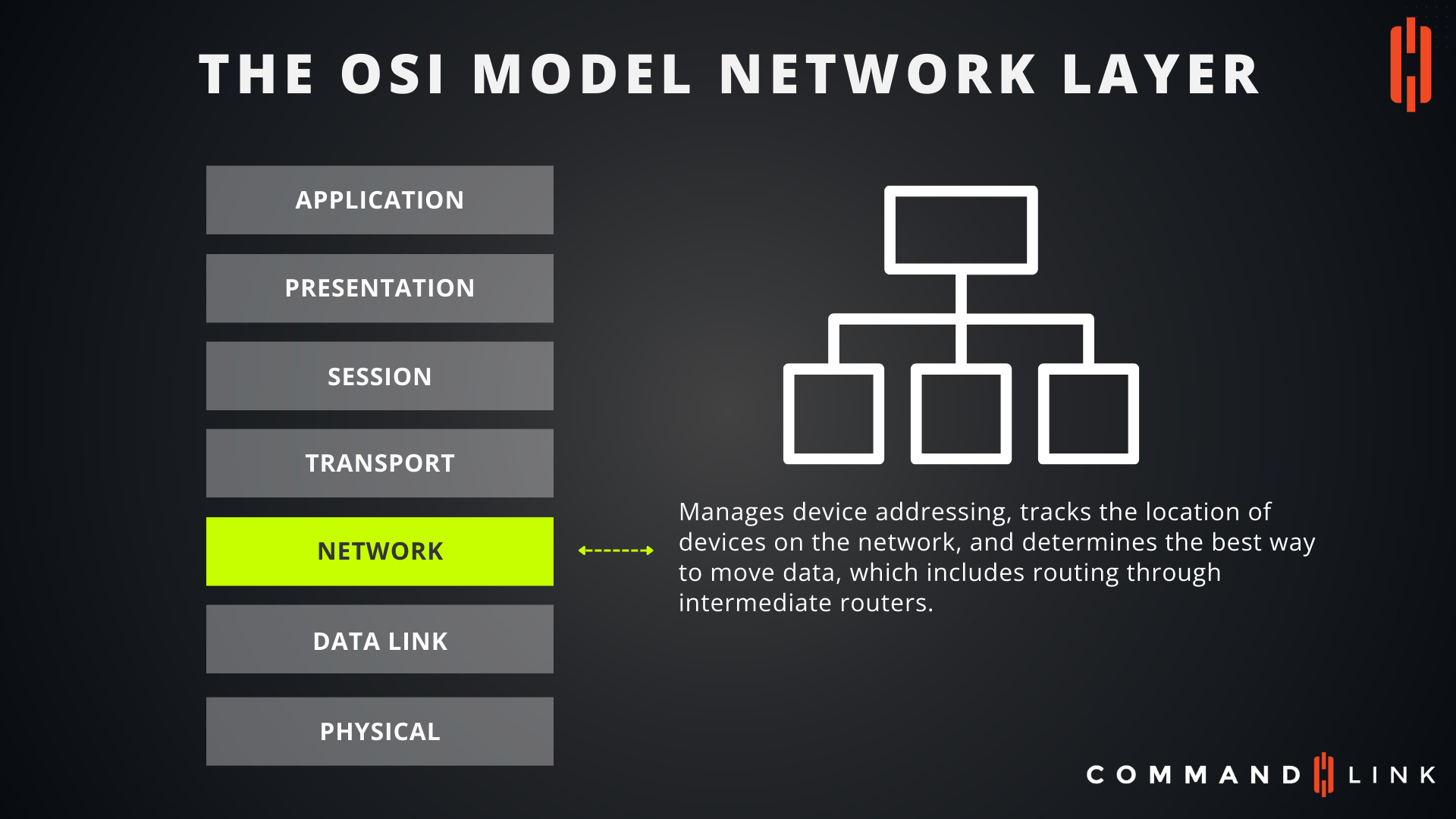
What Functions are Handled by the Network Layer of the OSI Model?
The Network Layer, which is the third layer of the OSI Model, is responsible for managing device addressing, tracking the location of devices on the network, and determining the best way to move data between these devices. It deals with logical addressing, routing, and packet forwarding, enabling data to travel from the source to the destination across various networks. This layer is critical in multi-network environments where data may need to traverse different networks to reach its destination. The Network Layer uses protocols such as IP (Internet Protocol) to route data and manage traffic control, ensuring efficient data transmission.
How Does the Network Layer Manage Routing in the OSI Model?
Routing is one of the primary functions of the Network Layer in the OSI Model. This layer determines the optimal path for data packets to travel from the source to the destination through various routers and networks. It uses routing tables and algorithms to calculate the most efficient route, considering factors such as network topology, traffic load, and the shortest path available. The Network Layer also handles packet fragmentation and reassembly, ensuring that large data packets are split into smaller fragments for transmission and reassembled at the destination.
What Role Does Logical Addressing Play in the Network Layer?
Logical addressing is a key function of the Network Layer, where each device on the network is assigned a unique IP address. This address serves as the identifier for the device, allowing it to be located and communicated with on the network. The Network Layer uses logical addressing to determine the best route for data packets to take, ensuring they reach the correct destination. Logical addresses are different from physical addresses (such as MAC addresses) because they can change as the network configuration changes, offering greater flexibility and scalability in network management.
Why is the Network Layer Critical for Inter-Network Communication?
The Network Layer is essential for inter-network communication, enabling data to be transferred across different types of networks. This layer acts as a bridge between networks, managing the routing of data packets across various routers and networks. It ensures that data can move seamlessly between networks of different structures and technologies, maintaining communication even in complex and dynamic network environments. Without the Network Layer, devices on different networks would struggle to communicate effectively, limiting the reach and efficiency of data transmission.
What Protocols Operate at the Network Layer of the OSI Model?
Several key protocols operate at the Network Layer of the OSI Model, with the most prominent being the Internet Protocol (IP). IP is responsible for addressing and routing packets across networks, ensuring that they reach their intended destination. Other protocols that operate at this layer include ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol), which handles error reporting and diagnostic functions, and IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol), which manages the membership of devices in multicast groups. These protocols work together to ensure reliable and efficient data transmission across complex network infrastructures.