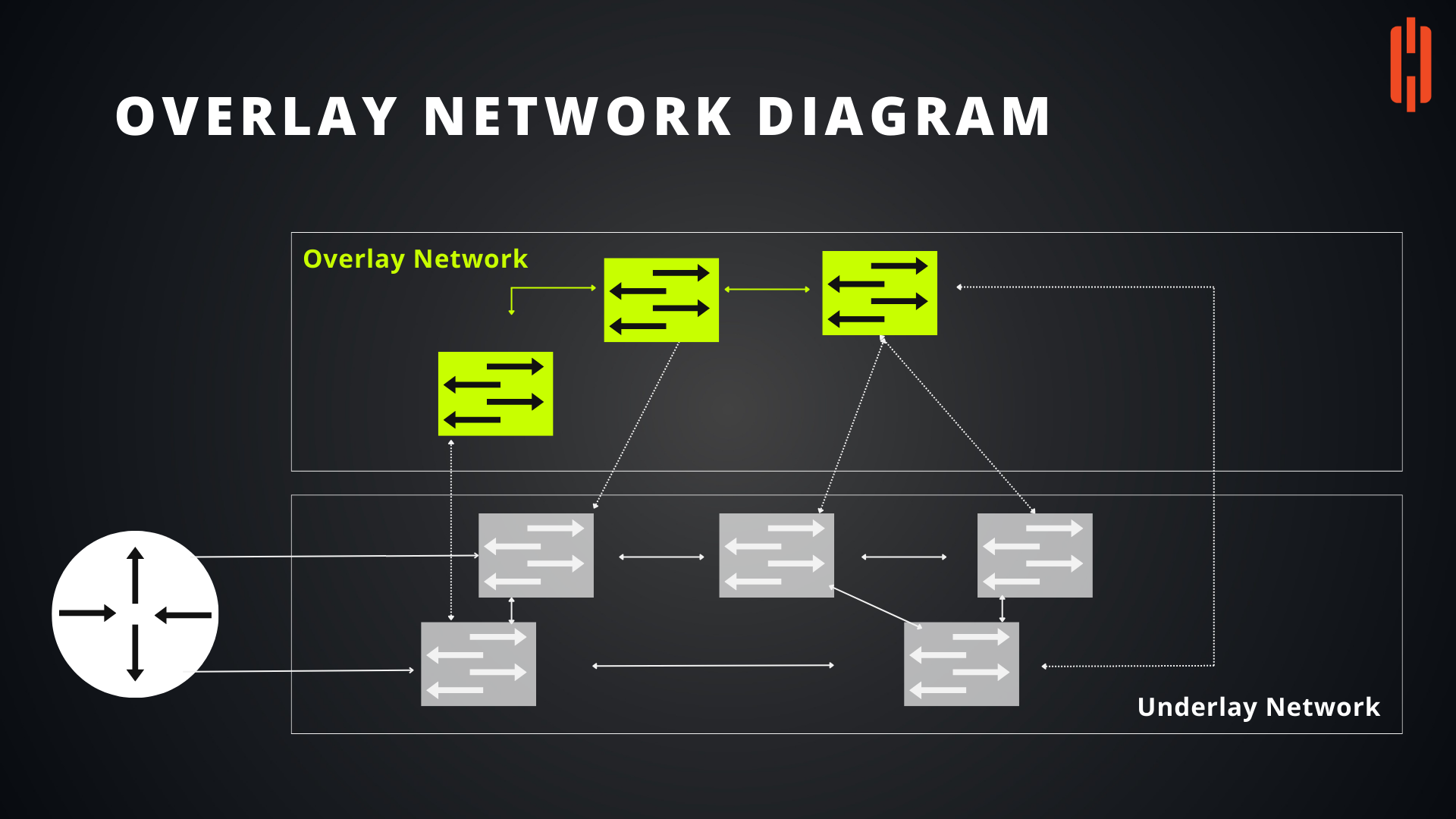
Understanding Overlay Network Diagrams: A Key Concept in Modern Networking
The image illustrates an overlay network diagram, a critical concept in networking, particularly in Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and SD-WAN architectures. Overlay networks provide a virtual network layer that runs on top of the existing physical infrastructure, or "underlay network." This separation of the logical and physical networks allows for greater flexibility, scalability, and control. Let’s break down the key components and functions depicted in the diagram.
What is an Overlay Network?
An overlay network is a virtual network that is built on top of another network, called the underlay network. The underlay network consists of the physical hardware and infrastructure, such as routers, switches, and cables, that facilitate the actual data transmission. The overlay network, on the other hand, is a logical layer that abstracts the physical network, allowing for the creation of virtual connections that can span across the physical infrastructure.
Components of the Overlay Network Diagram
- Overlay Network Layer (Highlighted in Green)
- Function: The overlay network layer represents the virtual connections and paths that are created on top of the underlay network. These virtual connections are not tied to specific physical routes, allowing for more flexible and efficient traffic management.
- Benefits: The overlay network enables advanced networking features such as traffic segmentation, virtual private networks (VPNs), and simplified network management. It allows for the dynamic routing of traffic based on real-time conditions, improving overall network performance and reliability.
- Underlay Network Layer (Depicted in Grey)
- Function: The underlay network is the foundational physical infrastructure that supports the overlay network. It includes all the physical devices and connections that handle the actual data transport.
- Benefits: The underlay network provides the necessary bandwidth, reliability, and performance needed to support the overlay network. It ensures that the data packets have a physical path to travel through, even if the logical path in the overlay network changes.
- Routing and Switching Elements (Arrows Indicating Data Flow)
- Function: The arrows in the diagram indicate the direction and flow of data between different network elements. In the overlay network, these paths can be dynamically adjusted based on policies, traffic conditions, and network demands.
- Benefits: Dynamic routing in the overlay network allows for more efficient use of network resources, reduced congestion, and improved application performance. It also enables features such as path redundancy and failover, ensuring higher availability.
- Separation of Control and Data Planes
- Function: In modern network architectures, the control plane (which makes decisions about where traffic should go) is often separated from the data plane (which actually moves the traffic). This separation is more evident in the overlay network, where control functions can be centralized for more efficient management.
- Benefits: Separating the control and data planes allows for more agile network management, easier implementation of security policies, and better optimization of network resources.
Why Use an Overlay Network?
- Scalability: Overlay networks can be easily scaled to accommodate new devices, users, or services without the need to overhaul the physical infrastructure.
- Flexibility: Virtual networks can be quickly reconfigured to adapt to changing business needs, such as new applications or changes in traffic patterns.
- Security: Overlay networks allow for the segmentation of traffic, which can enhance security by isolating sensitive data and applications.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By using the existing physical infrastructure more efficiently, overlay networks can reduce the need for expensive hardware upgrades.
Overlay networks represent a powerful tool in modern networking, enabling organizations to maximize the potential of their existing infrastructure while providing the flexibility and control needed to support dynamic business environments. Understanding the relationship between the overlay and underlay networks, as well as the benefits they offer, is essential for designing and managing efficient, scalable, and secure network architectures.